A search is under way to trace the stories of more than 30 fragments of the Stone of Destiny which separated from the ancient artefact after its famous theft from Westminster Abbey and secret repair.
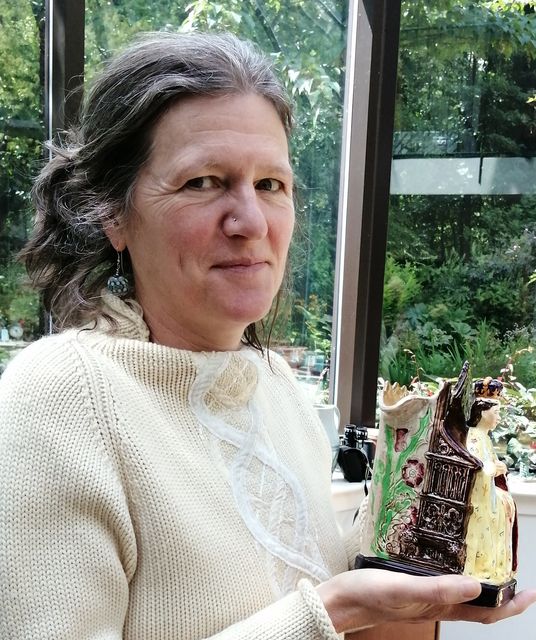
Professor Sally Foster has been painstakingly collating the history of as many of the pieces as possible, some of which were “hidden in plain sight”, saying they form a fascinating new strand in the centuries-old history of the Stone of Scone.
However, the exact location of most of these small chips remains a mystery as they have been passed down through families or are in private collections.
This has prompted Prof Foster to appeal to anyone who can help her research to come forward.
Many of the fragments in question came about when a mason secretly repaired the stone after it split in two during the raid by four students in 1950.
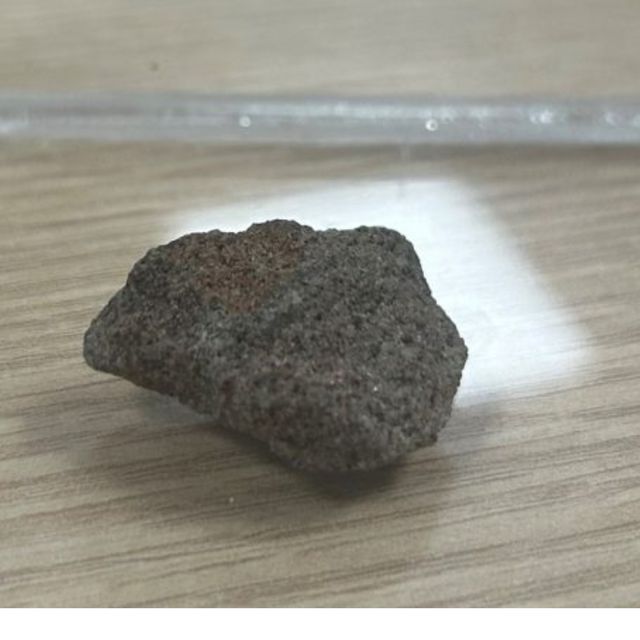
A fragment of the Stone of Destiny was gifted to Alex Salmond and was kept at the SNP’s headquarters (Ross Colquhoun/SNP/PA)
This work happened under the supervision of stonemason and nationalist politician Bertie Gray, who carefully numbered and recorded the pieces.
He passed them on to the four students who carried out the heist – as well as those he admired in and around the movement.
While the existence of fragments from the sandstone block returned in 1951 have been known – an inch-sized piece was gifted to Alex Salmond by Sir Neil MacCormick and was kept at SNP headquarters – it has not been widely appreciated that there are potentially more than 30 in existence.
Prof Foster believes Mr Gray’s repair work resulted in as many as 34 numbered fragments of the original stone.
The Commissioners for the Safeguarding of the Regalia – the body of senior officials charged with overseeing the Scottish crown jewels – are currently considering what should happen with the fragment gifted to Mr Salmond.
Prof Foster’s research, funded by the The British Academy and the Leverhulme Trust, has involved combing through old newspaper archives dating back decades.
Professor Sally Foster is appealing for people who may know the whereabouts of the fragments to get in touch with her (Sally Foster/PA)
It has revealed pieces of the stone in some surprising locations.
Other prominent nationalists to receive small chips include Margo MacDonald and Winnie Ewing – who had her piece fashioned into the centre of a brooch she once wore to an interview with the BBC’s David Frost.
Canadian journalist Dick Sanburn received chip number 25 in 1951 and proudly kept it behind his desk at the Calgary Herald. He said the fragments were “carefully numbered and recorded to prevent a flood of fakes”.
Former lord provost of Glasgow Sir Patrick Dollan displayed his chip to attendees at a concert in 1959.
Speaking to the PA news agency, Prof Foster said she met with the ccommissioners’ representatives last year after realising they may be making a decision about Mr Salmond’s fragment in “complete ignorance of the fact that there were others out there, beyond one that had came to light in 2018”.
She said: “Even at that stage I was aware there were other fragments, but I had not yet realised just many there were going to be.
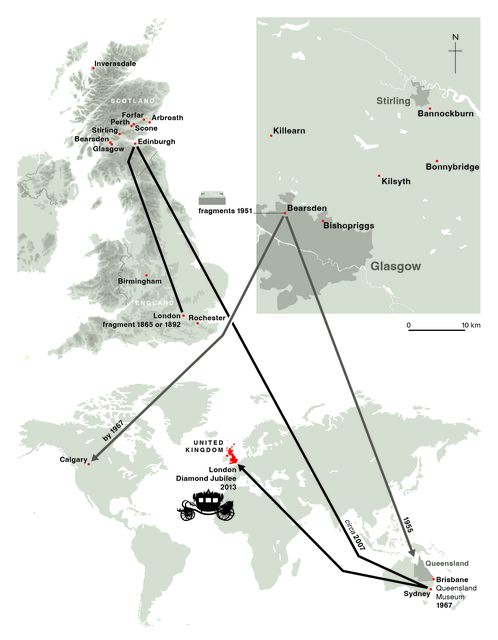
A graphic showing where various fragments of the Stone of Destiny have travelled (Christina Unwin/Sally Foster/PA)
“There was a case for codifying what their policy was going to be in relation to these, so that people wouldn’t feel shy about coming forth and say they’ve got – or had – a bit of it.”
She continued: “Each one of these things has got a fantastic story in its own right, telling us about the meaning of the stone for ordinary as well as famous people.
“Cumulatively, these offer valuable new perspectives to the enduring relevance of this national icon.”
As she continued her research project, titled Authenticity’s Child, Prof Foster discovered reports of more and more chips. Some were “hidden in plain sight”.
Up until his death in 1975, Mr Gray styled himself as the man who repaired the Stone of Destiny, but he never publicly revealed how many fragments he made.
Prof Foster is particularly interested in speaking to members of his family as they will likely be able to shed light on where some of the pieces are.
She is only completely sure about the locations of four fragments distributed by Mr Gray, who was influential in the Scottish Covenant Association which pushed for home rule.
The Stone of Destiny was repaired in secret (Russell Cheyne/PA)
While the stone itself is a particularly “unprepossessing” item, she argues that understanding the stories of these fragments adds a personal element to its narrative.
Prof Foster said: “It would be lovely to see more of these in the public domain and the stories being shared and celebrated.”
She has also tracked the fate of other, more official, fragments of the Stone of Scone which were taken as geological samples in the 19th century.
The Stone of Destiny was moved to its new home at Perth Museum last year, where it sits as the centrepiece of an exhibition on Scotland’s history.
When Charles was coronated in 2023 it was taken to London where it was mounted in the Coronation Chair, continuing its ancient role in the monarchy.
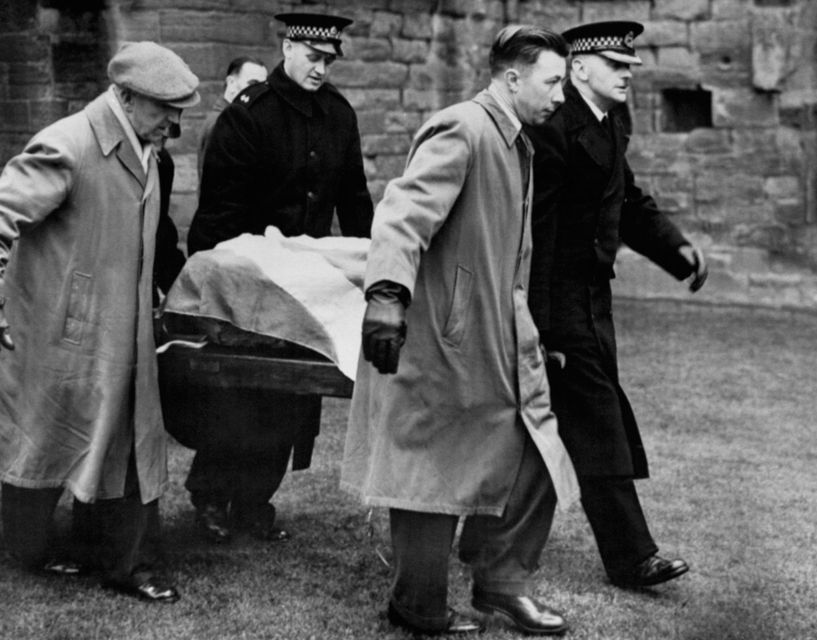
The 152kg sandstone block split in two during the famous Christmas Day raid of 1950, when four students spirited it back to Scotland to try and advance the cause of Scottish independence.
The Christmas raid in 1950 became famous, with the stone being returned in 1951 (PA Archive)
The repair work overseen by Mr Gray involved inserting three metal pins to help join the pieces back together, with a number of chips being created as a result.
The stone was recovered after a few months when it was left at Arbroath Abbey and the students who took it were never prosecuted – they maintained they were simply returning the artefact to Scotland.
Prof Foster can be contacted on her project’s website – thestone.stir.ac.uk – or via Stirling University.
A Scottish Government spokesman said: “The Scottish Government welcomes Professor Foster’s report and we are liaising with her over this research.
“The fragment is currently being held by Historic Environment Scotland on behalf of the Commissioners for the Safeguarding of the Regalia, as agreed when the fragment was submitted for analysis.
“The commissioners are considering options for the future location of the fragment. A final decision will be made in due course.”